Incoterms
Delivery Methods in International Trade
In international trade, it is important to clearly determine the obligations of the buyer and seller, such as where the goods will be delivered, who will bear the expenses or how they will be shared, whether insurance and transportation contracts will be made or not.
One of the useful sources on this subject is INCOTERMS (International Commercial Terms) published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). INCOTERMS is a set of internationally accepted rules used in contracts between buyer and seller, showing the responsibilities of the buyer and seller.
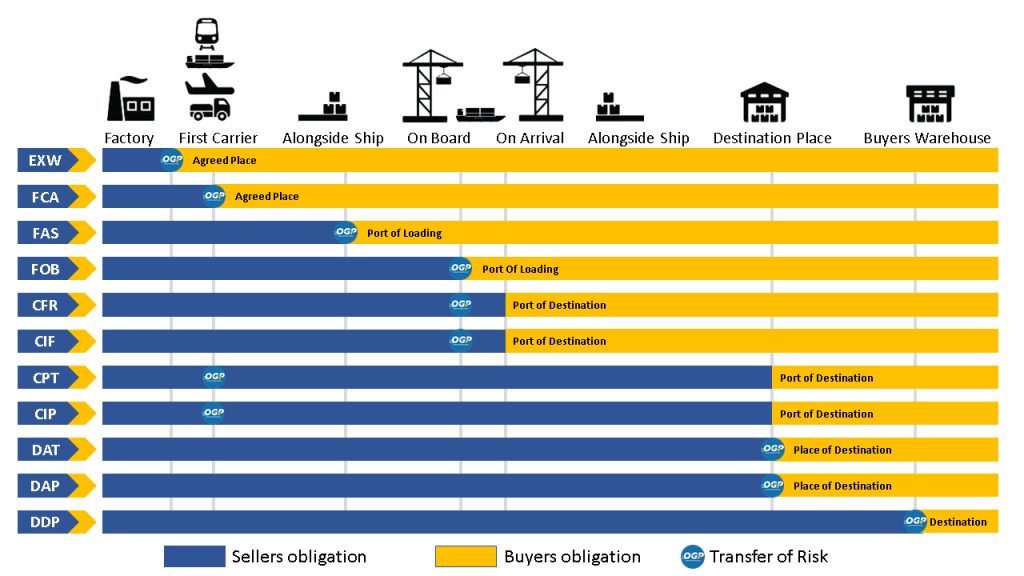
The latest INCOTERMS 2010 was published by ICC. Accordingly, there are 11 delivery methods in international trade and they are divided into two classes.
– Rules covering all transport types: EXW, FCA, CPT, CIP, DAT, DAP, DDP
– Rules specific to sea and inland water transport: FAS, FOB, CFR, CIF
DELIVERY AT WORKS / EX WORKS (EXW)
In this type of delivery, the seller delivers the goods by leaving them at the disposal of the buyer at his own place or at another named place (such as a factory, warehouse, workplace). The seller is not obliged to load the goods on any transportation vehicle. From the moment of delivery of the goods, all costs and risks related to the goods are borne by the buyer. In this form of delivery, there is minimal liability on the part of the seller.
FREE CARRIER (FCA)
In this type of delivery, the seller delivers the goods to the carrier or another person appointed by the buyer at the seller’s workplace or another designated place. In this type of delivery, the seller must complete the export customs procedures of the goods at his own expense and damage. All costs and risks related to the goods pass to the buyer from the moment of delivery.
FREE ALONGSIDE SHIP (MOROCCAN)
In this type of delivery, the seller delivers the goods by leaving them at the designated loading port, in line with the ship selected by the buyer (for example, on a dock or on a barge). If the goods are at the ship dock, by bringing them to the loading place; If the ship is anchored offshore, it is delivered to the ship by barges. Damage and expenses related to the goods pass to the buyer when the goods are left in line with the ship, and the buyer bears all expenses from that moment on. The seller obtains any export permit or other official permissions required for the export of the goods at his own risk and expense, and completes the necessary customs procedures for the export of the goods.
FREE ON BOARD (FOB)
This delivery method is the most used in our country; The seller delivers the goods at the designated loading port, on the ship selected by the buyer or by providing the goods delivered in the specified manner. Damage and expenses related to the goods pass to the buyer when the goods are on the ship, and the buyer bears all expenses from this moment on. The seller obtains any export permit or other official permissions required for the export of the goods at his own risk and expense, and completes the necessary customs procedures for the export of the goods.
COST AND FREIGH (CFR)
In this form of delivery, the seller delivers the goods on board or supplies the goods already delivered in this way. Damage and costs related to the goods pass to the buyer when the goods are on board the ship. The seller, at his own risk and expense, obtains any export permit or other official permissions required for the export of the goods and completes the necessary customs procedures for the export of the goods. The seller concludes a transportation contract to bring the goods to the designated port of destination and pays the costs and freight.
COST, INSURANCE AND FREIGHT (CIF)
In this form of delivery, the seller delivers the goods on board or supplies the goods already delivered in this way. Damage and costs related to the goods pass to the buyer when the goods are on board the ship. The seller, at his own risk and expense, obtains any export permit or other official permissions required for the export of the goods and completes the necessary customs procedures for the export of the goods. The seller concludes a transportation contract to bring the goods to the designated port of destination and pays the costs and freight. The seller also enters into an insurance contract against the buyer’s risk of loss and damage to the goods during the journey.
CARRIAGE PAID TO (CPT)
In this type of delivery, the seller delivers the goods to the carrier he has personally chosen and made an agreement with, after the customs procedures for the export of the goods have been completed, the necessary transportation contract to be sent to the specified destination has been made and the transportation costs have been paid. The seller, at his own risk and expense, obtains any export permit or other official permissions required for the export of the goods and completes the necessary customs procedures for the export of the goods.
CARRIAGE AND INSURANCE PAID / CARRIAGE AND INSURANCE PAID (CIP)
In this type of delivery, the seller delivers the goods to a carrier or other person provided by him at the registered place, and the seller concludes the contract of carriage and pays the transportation costs for the goods to reach the specified destination. The seller obtains, at his own expense, any export permit or other official permission required for the export of the goods and completes the necessary customs procedures for the export of the goods. The seller pays the transportation time and expenses, as well as the freight, for the goods to be registered and distributed to the port of destination. The seller also enters into an insurance contract against the risk of loss and damage to the goods during the buyer’s travels.
DELIVERED AT TERMINAL (DAT)
In this type of delivery, the seller delivers the goods by leaving them at the disposal of the buyer, unloaded from the incoming transportation vehicle at the designated terminal at the designated destination or port. The term terminal includes any place that may be uncovered or covered, such as a dock, warehouse, container yard or road, rail or air cargo station. The seller, at his own risk and expense, obtains any export permit or other official permissions required for the export of the goods and completes the necessary customs procedures for the export of the goods. The seller concludes a transportation contract to bring the goods to the designated port of destination and pays the costs and freight. The seller also assumes all damages and costs associated with bringing the goods to the named place of destination or port and unloading them from the means of transport.
DELIVERED AT PLACE (DAP)
In this type of delivery, the seller delivers the goods at the specified destination, leaving them at the disposal of the buyer without unloading them from the incoming transportation vehicle. The seller assumes all damages and costs related to the delivery of the goods to their destination. The seller, at his own risk and expense, obtains any export permit or other official permissions required for the export of the goods and completes the necessary customs procedures for the export of the goods. The seller concludes a transportation contract for the transportation of the goods to the specified delivery point, if any, to the agreed point, at his own expense. The seller assumes all damage and expenses related to the delivery of the goods to the specified destination.
CUSTOMS DUTIES PAID / DELIVERED DUTY PAID (DDP)
In this type of delivery, the seller delivers the goods at the disposal of the buyer, customs-cleared for import and ready to be unloaded on the transport vehicle at the designated destination. The seller undertakes all damages and expenses related to the delivery of the goods to the specified destination, is obliged to carry out customs clearance not only for the export but also for the import of the goods, pay all duties necessary for export and import and fulfill all customs formalities. There is maximum liability for the seller.